
Communication and sharing promote growth
Joining Hands for Development!

The air tightness of the battery pack is a key factor in ensuring the quality and safety of the battery pack. It is related to the safety, reliability and service life of the battery pack. The air tightness test of the battery pack should be carried out not only during the production process, but also during battery maintenance and inspection.
1-Battery Pack Airtightness Requirements
In actual production, the air tightness of the battery pack must meet the following requirements:
Sealing performance, the battery pack shell, interface and connectors must have good sealing performance to prevent dust, water vapor and other external impurities from entering the battery pack, which can be achieved through welding, sealants, waterproof materials, etc.
Waterproof performance, to prevent moisture from entering the battery, causing short circuits, corrosion and other problems. According to the national standard GB38031-2020 "Safety Requirements for Power Batteries for Electric Vehicles", the sealing performance of batteries and their components should meet the IP67 standard. Most new energy vehicles have higher sealing performance requirements for batteries and their components, and must meet the IP68 standard, that is, the battery pack can prevent water from entering within the specified water depth and submersion time.
Traditional air tightness testing methods include pressure method and immersion method (water test). The immersion method is to immerse the liquid cooling plate in water and observe whether bubbles are generated to judge the sealing.

Liquid Cooling Plate Water Channel Air Tightness Test Tank
Although the IP68 standard is more stringent, in actual applications, the pressure drop method is often used as the main detection method to meet the IP68 requirements by setting appropriate airtightness detection standards. The pressure drop method determines the airtightness of the battery pack by measuring the pressure change inside the battery pack. When performing airtightness testing, multiple parameters need to be paid attention to, such as inflation pressure, inflation time, pressure stabilization time and leakage rate.
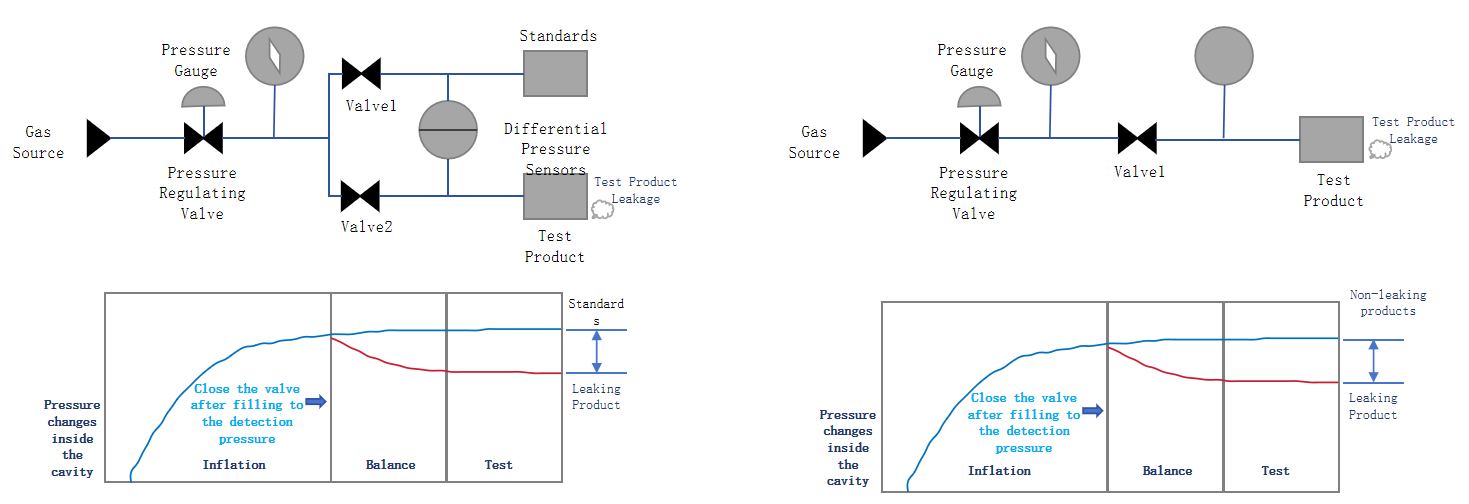
Differential pressure basic principle diagram Direct pressure basic principle diagram
2-Analysis of Liquid Cooling Plate Leakage Problem
With the continuous upgrading of market demand for power battery vehicles, battery energy storage systerms, etc., higher energy density and power density battery packs are widely used. Because of the thermal characteristics of batteries, to ensure the stable operation of core equipment such as batteries and improve energy utilization efficiency, liquid cooling technology is one of the mainstream technical routes for energy storage thermal management, and the air tightness test of the liquid cooling system has become a key link.
Liquid cooling plate leakage is a serious problem: the leakage will hinder the normal flow of the coolant, affect the heat dissipation effect of the liquid cooling plate, and reduce the performance of the equipment; the leakage may also cause aging and damage of system components, reducing the reliability of the system; the leakage may also corrode electronic components and circuits, increasing the risk of equipment failure and fire.
Why does the leakage problem still occur after rigorous air tightness testing during the production and manufacturing process of the liquid cooling plate?
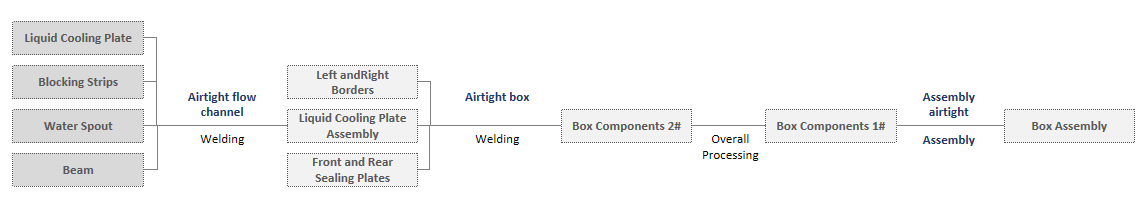
Liquid Cooling System Airtightness Test Process
Liquid seepage may be caused by a variety of factors:
l Tiny cracks and defects. Landscape air tightness testing may detect large leakage channels, but tiny cracks and defects may still exist. These tiny cracks may expand under liquid pressure or high temperature environment, causing liquid seepage.
l Coolant surface tension and wettability differences: When the surface tension of the coolant is low, it is easier to penetrate through tiny gaps. If the surface tension design of the liquid cold plate is unreasonable or the coolant is not properly selected, the liquid seepage problem may be aggravated.
Wettability differences: Different coolants have different wettability on solid surfaces. If the material surface roughness of the liquid cold plate is high or there are microstructural defects, the coolant may penetrate more easily.
l Installation or process problems: If the installation process of the liquid cold plate is not fine enough, or there are defects in the welding, connection and other processes, it may also lead to poor sealing and increase the possibility of liquid seepage.
l Environmental conditions: Changes in temperature, especially in high-pressure environments, may affect the permeability of the coolant. Although these environmental factors may not be considered during air tightness testing, in actual operation, temperature fluctuations may cause seal failure.
l Material aging or fatigue: If the material of the liquid cold plate is used for too long, it may age or fatigue, causing its sealing performance to deteriorate, thereby increasing the risk of liquid leakage.
3-Preventive Measures for Liquid Cooling Plate Leakage
l Improve the design of liquid cooling plate: By optimizing the structure and design of the liquid cooling plate, reduce small cracks and defects, and improve its sealing performance. For example, when welding the module installation beam on the flow channel surface, take anti-leakage measures to avoid coolant leakage.
l Improve the manufacturing process level: In the production process of the liquid cooling plate, high-quality welding processes and materials are used to ensure that the coolant is not easy to penetrate. At the same time, during the assembly process, strictly follow the operating procedures to avoid looseness or incorrect installation.
l Optimize the combination of detection methods to ensure detection efficiency while improving detection accuracy and reducing missed detection rate. The immersion method and pressure drop method are used for air tightness detection, which is simple to operate, economical, and efficient, and is suitable for large-scale routine detection needs. However, the detection accuracy of the two methods is low. The detection accuracy of the pressure drop method is generally a leakage rate of 1×10-4Pa·m³/s, and the accuracy of the detection results is easily interfered by factors such as temperature, humidity, cleanliness, and pressure. Use detection equipment with higher detection accuracy and better effect to increase the detection accuracy to 1×10-6Pa·m³/s, thereby improving the detection effect.
In addition to the preventive measures for the liquid cooling plate itself, it is also necessary to adopt appropriate response strategies in multiple aspects such as coolant selection, seal selection and equipment working environment.
We will regularly update you on technologies and information related to thermal design and lightweighting, sharing them for your reference
Thank you for your attention to Walmate