
Communication and sharing promote growth
Joining Hands for Development!

As a key component of the liquid cooling system, the design of the water block must take into account multiple factors such as heat exchange performance, structural strength, corrosion resistance, leakage resistance, and cost control. The water block is usually designed with a complex heat exchange slot structure (i.e., flow channel), and the quality of its internal flow channel design directly determines the heat exchange efficiency of the entire system.
Part 2:Water block design, processing technology and challenges
1-Design requirements for water blocks in different scenarios
l High Performance Computing:
High-performance computing devices (such as high-performance CPUs, GPUs, etc.) generate a lot of heat during operation, so the water block needs to have efficient heat dissipation capabilities. In order to meet the high heat flux density heat dissipation requirements, the water block usually adopts a high-density microchannel design to increase the heat exchange area and improve the heat dissipation efficiency. In addition, some designs integrate the water block directly onto the CPU, eliminating the step of applying silicone grease, which not only simplifies the assembly process, but also further improves the heat dissipation performance. In terms of reliability, the water block must have excellent sealing performance to prevent leakage and ensure long-term stable operation.
l Graphics card cooling:
Graphics cards are high heat generating areas, so the water block needs to have a full coverage design to ensure that all heat generating components on the graphics card can be effectively cooled. At the same time, graphics card cooling requires a high flow rate of coolant, so the internal structure of the water block needs to support high flow rate to quickly remove heat.
l Data Center:
In data centers, the structural design of water block needs to meet multiple requirements such as efficient heat dissipation, low noise, high reliability, adaptability to high power density, intelligent management and environmental adaptability to ensure stable operation and efficient heat dissipation of data centers.
2- Evolution trend of water block structure
The evolution trend of water block structural design reflects the dual pursuit of technological innovation and performance improvement, which is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
l Improved heat dissipation performance:
Increase contact area: Some water block designs improve heat dissipation performance by increasing the contact area with the heating element. For example, a large-area copper base design can achieve good contact and heat conduction.
Optimize the internal structure: Optimize the internal water channel. One idea is to optimize the fluid flow, such as changing from ordinary fins to steering fins, presenting a long strip flow channel, promoting flow boundary layer separation, reducing boundary layer thickness, and improving heat exchange efficiency; another idea is to increase the heat capacity area, such as changing from traditional coarse water channels to microchannel design, which significantly increases the contact area between the coolant and the base plate and enhances the heat dissipation efficiency. In some designs, the coolant is sprayed onto the microchannel base plate through a guide plate to increase the local flow velocity and turbulence, greatly improving the heat absorption efficiency.
l Integrated and intelligent design:
Integrated design: The integrated design integrates the water pump, heat sink fins, heat conduction base and other components together to reduce the number of connection points and improve system stability and heat dissipation efficiency.
Multifunctional integration: In addition to heat dissipation performance, modern water blocks also have temperature display and monitoring functions.
Modular design: The modular buckle structure improves the convenience and freedom of organization.
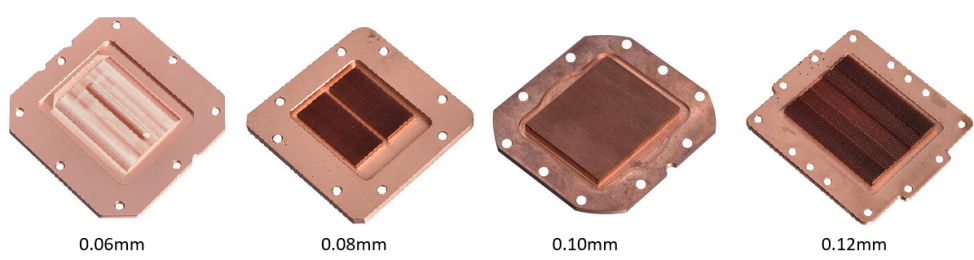
Figure 1: Water block base with different fin thicknesses
l High-performance materials and finishes:
The use of high-performance materials such as pure copper base, combined with surface treatment technologies such as nickel plating, improves thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance.
3-Processing technology and challenges
l Material properties affect processing:
Material hardness and toughness issues: Radiators made of different materials, such as copper, aluminum and their alloys, have different hardness and toughness, and different requirements for processing tools and processes. Materials with higher hardness will wear faster and require more frequent tool changes; materials with better toughness are prone to deformation and burrs during cutting.
The processing of copper-aluminum composite materials is complex: copper-aluminum composite material shovel-tooth heat sinks must first be made into composite materials using continuous casting semi-molten state pressing technology, and then shovel-tooth processing is performed. The process is more complicated and requires higher precision for equipment and processes.
l High dimensional accuracy requirements
It is difficult to ensure the consistency of tooth height and thickness: For some high-density tooth heat sinks, the height and thickness of each tooth are required to be highly consistent to ensure the performance and uniformity of the heat sink. If the difference in tooth height and tooth thickness is too large, it will lead to uneven heat transfer and affect the heat dissipation effect. During the processing, high-precision equipment and automated control systems are required to ensure that the specifications of each tooth are consistent.
It is difficult to control the tooth spacing: When the teeth on the heat sink are too dense, their density and spacing make the processing process more complicated, and the processing equipment needs to have higher speed and precision to maintain the uniformity of the teeth. For example, when the tooth spacing is too small, the tool is prone to interference during cutting, affecting the processing accuracy and surface quality.
l Strict surface quality requirements
Burr problem: Burrs are easily generated during the processing, which not only affects the aesthetics of the radiator, but also may hinder air flow and reduce the heat dissipation effect. The generation of burrs may be caused by low material cutting accuracy, wear of processing tools, etc., and corresponding deburring processes need to be adopted to solve them.
Surface roughness: The surface roughness of the radiator affects its heat dissipation performance and subsequent surface treatment effects. Excessive surface roughness will increase the resistance to air flow and reduce heat dissipation efficiency. Additional surface treatment is required to reduce the roughness, which increases processing costs and time.
l High processing equipment and process requirements
Equipment accuracy and stability: Gear shoveling requires a high-precision gear shoveling machine, and the accuracy of the equipment directly affects the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of the teeth. At the same time, the equipment must have good stability to ensure dimensional consistency during long-term processing.
Tool selection and wear: Suitable tools are crucial to processing quality. The material, geometric parameters, etc. of the tool need to be selected according to the material properties. During the processing process, tool wear will lead to increased cutting force, decreased dimensional accuracy and increased surface roughness, and the tool needs to be adjusted or replaced in time.
Feed speed and cutting depth: Unreasonable settings of feed speed and cutting depth can easily lead to processing defects. If the feed speed is too fast and the cutting depth is too large, the tool will be overloaded, resulting in tool snatching, tool bounce, tool drop, etc., affecting processing accuracy and surface quality.
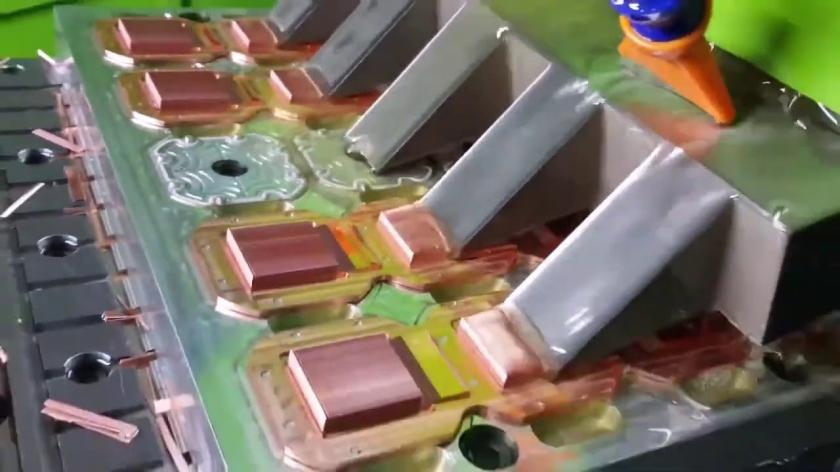

Figure 2: Skiving process
l High customization requirements
Different application scenarios have different requirements for the size, shape, tooth height, tooth thickness, tooth spacing and other parameters of the radiator, which need to be customized according to specific needs. This requires the processing manufacturer to have flexible process adjustment capabilities and rich experience to meet diverse customization needs.
We will regularly update you on technologies and information related to thermal design and lightweighting, sharing them for your reference.Thank you for your attention to Walmate.